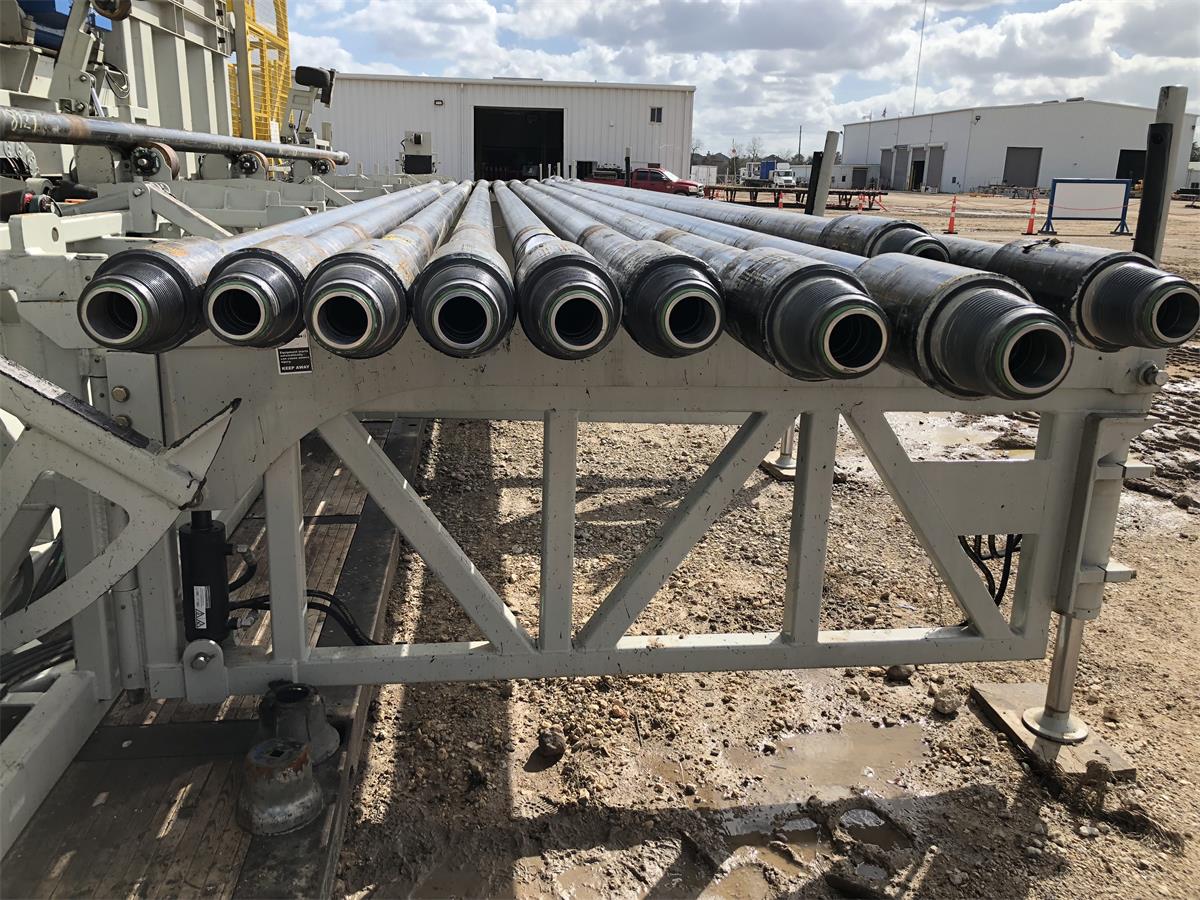
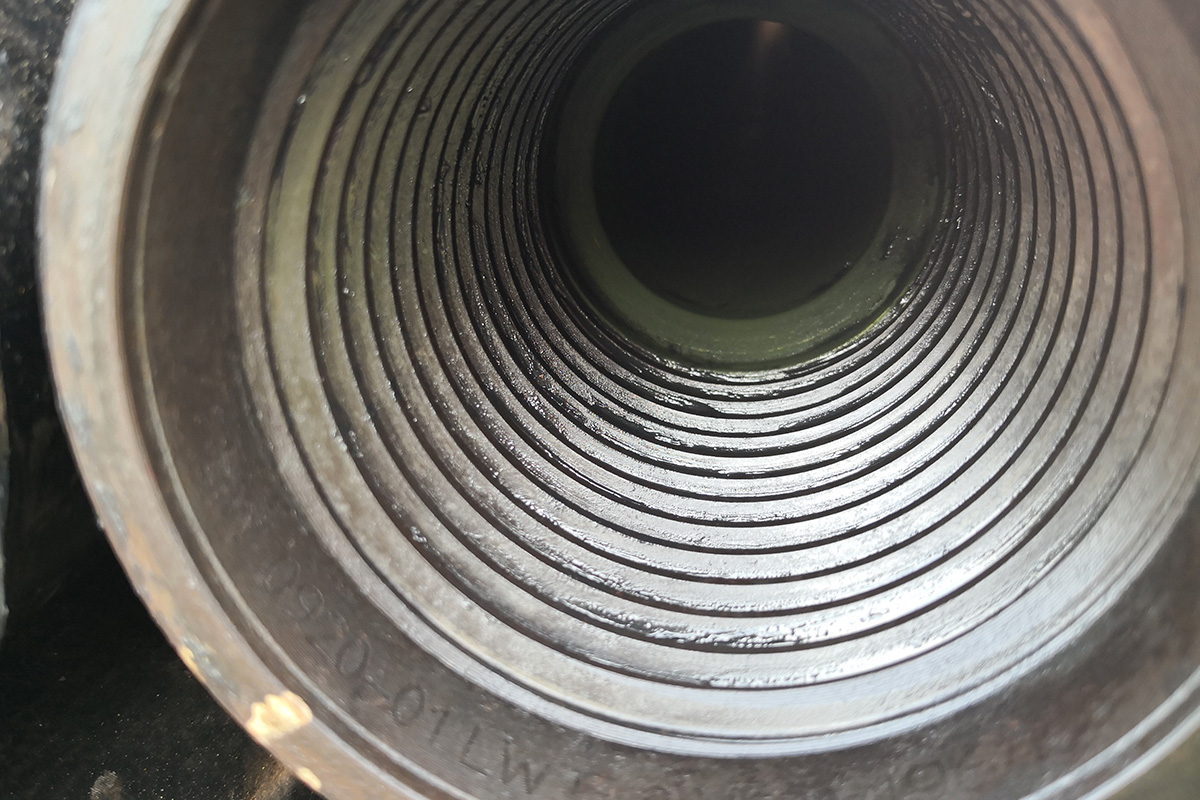
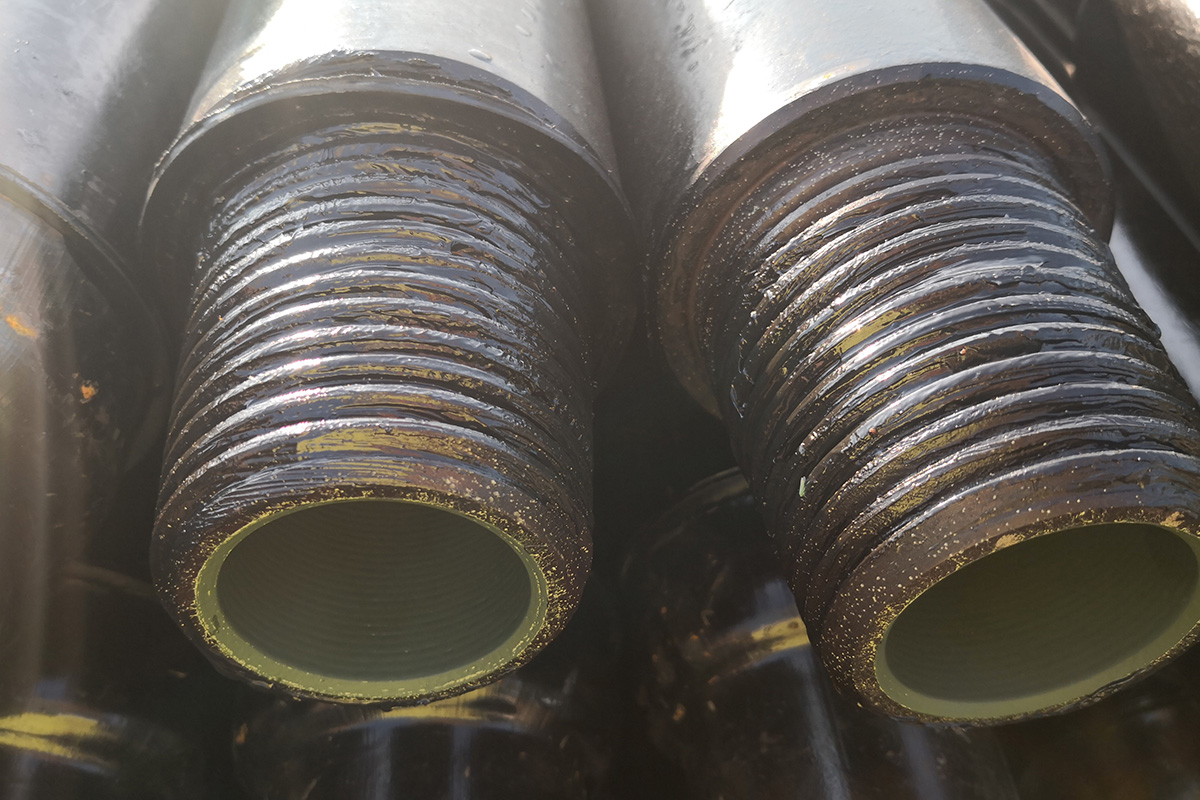
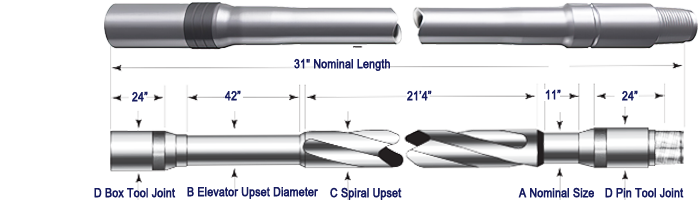
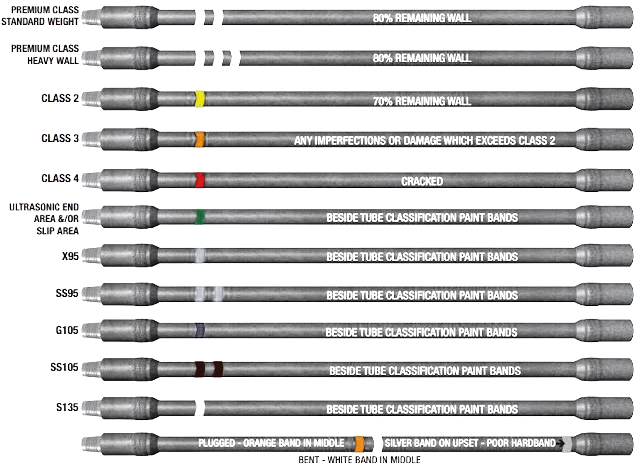
Drill Pipe
Products: Drill Pipe, Heavy Weight Drill Pipe, Drill Collar
Size: 2-3/8"--6-5/8"
Standard: API 5DP
Grade: E75, G105, S135, SS-105, X95, X57, X75, X39
Length: Range 1, Range 2, Range 3
Upset of Drill Pipe:
Internal Upset IU
External Upset EU
Internal-External Upset IEU
Thread/Connection Types of Drill Pipe:
NC26, NC31, NC38, NC40, NC46, NC50, 5-1/2 FH, 6-5/8 FH
XT Connection of Drill Pipe:
XT connections facilitate the use of larger drill pipe in a set hole size, such as 5⅞ in. drill pipe with XT 57 in an 8½ in. hole size.
X57, X75, X39, X95
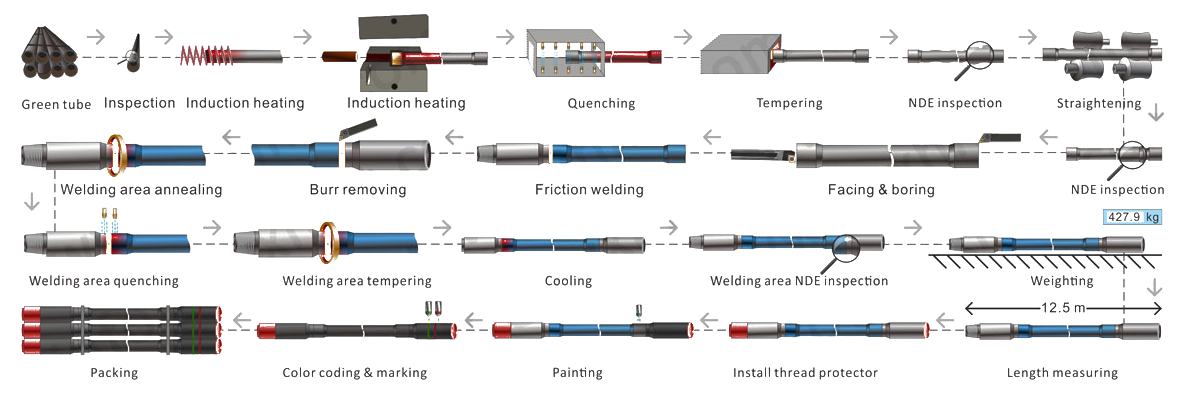
Details of manufacturing:
Tool joints are inertia welded to the tubes with computer-monitored precision. Concentricity is carefully monitored and controlled, and the parameters of each weld are electronically recorded, and traceable to each joint. After removal of weld flash, the weld area is austenitized, quenched, and tempered to achieve the required mechanical properties. Heat treat cycles for each weld are compared to specific parameters and recorded for traceability. After all steps and machine marks are polished from the OD and ID area, hardness testing, ultrasonic testing, and wet magnetic particle inspections are used to verify the integrity of each weld zone.
Drill-pipe corrosion:
Drill-pipe corrosion is a critical issue for any drilling operation, particularly under high-pressure, high-temperature downhole conditions. However, most laboratory studies have been conducted under ambient and static conditions, with only a few downhole studies based on flow loop showing inconsistent results. In this study, we proposed a novel simple method to simulate pipe corrosion/erosion in a reservoir-like environment under both the static and dynamic conditions and investigated the influences of wellbore conditions, including temperature, pressure and salinity of water-based drilling fluids, on the corrosion behaviour of the drill pipe. The results showed that the erosion effect of the drilling fluid (without drilled cuttings) was negligible. Furthermore, we found that the corrosion rate increased with an increase in the temperature, pressure and rotational speed; however, it decreased with an increase in the salinity. In addition, the proposed method can be used to simulate other complicated conditions.
- Country of origin
- China